IS:trainDetector
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
trainDetector
Schema description / Schemabeschreibung
Position of trainDetector in the XML-Tree / Position von trainDetector im XML-Baum
- Parent: <trainDetectionElements>
- Children: <additionalName> (introduced with version 2.1), <any>, <geoCoord>, <states>
Multiplicity / Anzahl
Semantics / Bedeutung
A <trainDetector> allows for defining axle counter, hot axle detectors...
Attributes of trainDetector / Attribute von trainDetector
- id: XML-file-wide unique, machine-interpretable identity, required for later referencing that element internally. For a detailed explanation see Dev:identities.
XML-Datei-weit eindeutige, maschineninterpretierbare Identität, die für die spätere interne Referenzierung dieses Elements erforderlich ist. Für eine detaillierte Erklärung siehe Dev:identities. - code (introduced with version 2.1): Machine-interpretable string (e.g. an abbreviation) used for identification of the object across exchange partners, usecase specific uniqueness constraints may apply. Please see our description of the differences between id, code and human-readable identifiers.
Maschineninterpretierbare Zeichenkette (z.B. Abkürzung), die zur Identifizierung des Objekts auch bei Austauschpartnern verwendet wird, wobei spezifische Eindeutigkeitsbeschränkungen gelten können. Bitte beachten Sie unsere Erläuterung zu den Unterschieden zwischen id, code and menschenlesbaren Kennzeichnungen. - name: Established, human-readable short string, giving the object a name. Not intended for machine interpretation, please see our notice on human interpretable data fields.
Etablierte, menschenlesbare kurze Zeichenkette, die das Objekt benennt. Nicht zur maschinellen Interpretation bestimmt, siehe Hinweise zu menschenlesbaren Datenfeldern. - description: Human-readable, more detailed description as addition to the name. It should give additional explanations or hints to the contents of this element. Not intended for machine interpretation, please see our notice on human interpretable data fields.
Menschenlesbare, detailliertere Beschreibung als Ergänzung zu name. Sie soll zusätzliche Erläuterungen oder Hinweise auf den Inhalt dieses Elements geben. Nicht zur maschinellen Interpretation bestimmt, siehe Hinweise zu menschenlesbaren Datenfeldern. - xml:lang (introduced with version 2.1): This is a unique identifier of language. It uses basically the language standard IETF BCP 47 (external link) which may be different to ISO 639-1 (external link) or ISO 639-2 (external link). For mapping hints see relation to other standards (external link).
This defines the language used for name and description. Use <additionalName> to provide a name and/or description in other languages.
- pos: This is the position on a track defined as distance from its start (trackBegin) regardless the "absolute mileage" in @absPos.
Das ist die Position des Elements auf einem Track i.S. der realen Entfernung zum trackBegin. Sie ist damit unabhängig von der mit absPos modellierten Strecken-Kilometrierung.
|
- absPos: This is the position on a track as absolute mileage/chainage.
Das ist die Position des Elements im Referenzsystem der Strecken-Kilometrierung.
|
- absPosOffset (deprecated with version 2.1): The semantics of this attribute aren't very clear. It seems to be redundant to the definitions with mileageChanges in "overlapping regions".
- dir: This defines the validity of trainDetector along the track. Possible values are:
- up: This denotes the direction from the <trackBegin> to the <trackEnd> (increasing relative position values).
- down: This goes opposite to up (decreasing relative position values).
- unknown: trainDetector is restricted to a certain direction, but this direction is not known.
- ocpStationRef: This refers to the id attribute of the associated <ocp> element.
(introduced with version 2.1)
- controllerRef: This refers to the id attribute of the associated <controller> element.
(introduced with version 2.1)
- detectionObject Possible values are:
- wheel the track circuit confirms the absence of a train to the signalling system (track circuit clear). The presence of metal wheels and axles of a train within the track circuit boundaries will cause the rails to be ‘short circuited’ [1]
- axle a system using counting points and a counter which detects the occupancy of a section of track by comparing the number of axles which enter the section with the number of axles which leave the section, parity of the numbers being necessary to give a clear indication.
- train Train-borne positioning systems are a feature of modern Communication-Based Train Control systems (which often use moving block technology). These systems rely on the train regularly reporting its location and other information to the control centre, for which of course it requires a reliable communication link[1]
- endOfTrain device for an electronically controlled pneumatic brakes (ECP) brake system that is physically the last network node in the train, pneumatically and electrically connected at the end of the train to the train line cable operating with an ECP brake system. For further details, see [2]
- obstacle Obstacle detecting via cameras
- other:anything: Any value that does not fit any value from the previous enumeration list, fulfilling the constraint: at minimum two characters, whitespace is not allowed. Please, apply Dev:usingAny accordingly.
- medium Possible values are:
- mechanical mechanical equivalent of a short track circuit. An example is a fouling bar that is fixed to the running rail in such a manner as to allow the wheel flanges of any vehicle passing over it to depress it to an amount equal to the depth of the wheel flange. [3]
- hydraulic installed below the rails and detect the slight bending of the rail caused by the presence of a large mass. This force is amplified by a liquid [4]
- pneumatic same as "hydraulic" but the force is amplified by a gas.
- magnetic uses a magnetic field to detect the passage of the rim and flange of a wheel.
- inductive uses inductive sensors to detect a train. It can be a kind of axle counter.
- optical used when one detects train by cameras
- radio data-enabled radios (e.g. 4G/LTE) are used for the ground to train communications. This value should not be used because radio is used to transmit information rather than to detect a train.
- manual: (introduced with version 2.5) used when a person goes to the railway track to detect a train
- other:anything: Any value that does not fit any value from the previous enumeration list, fulfilling the constraint: at minimum two characters, whitespace is not allowed. Please, apply Dev:usingAny accordingly.
- posInTrack Possible values are:
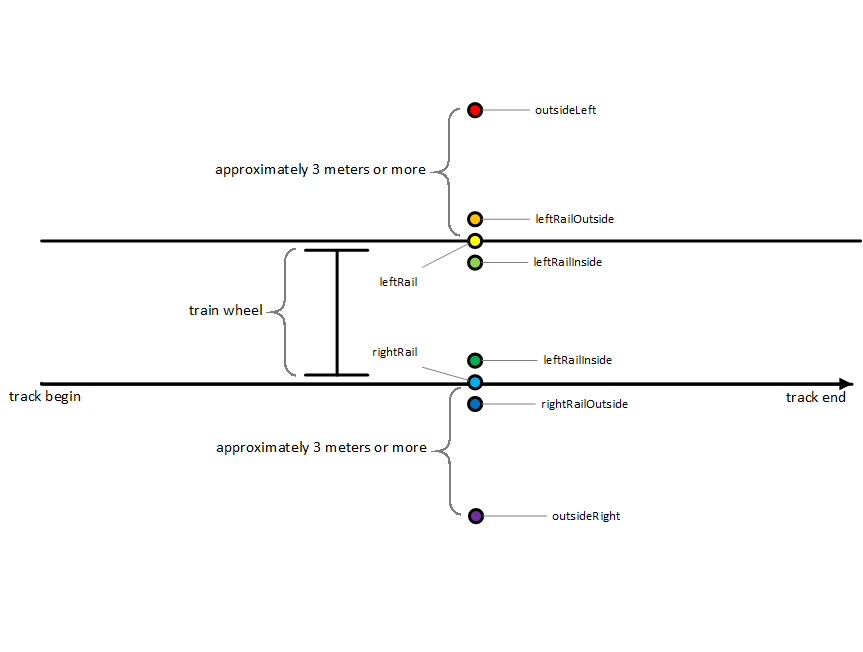
- center used when the train detector is placed in the middle of the track. See the posInTrack drawing for reference.
- leftRail used when the train detector is placed on the top of the left rail. See the posInTrack drawing for reference.
- leftRailInside used when the train detector is placed near the left rail inside the track. See the posInTrack drawing for reference.
- leftRailOutside used when the train detector is placed near the left rail outside of the track. See the posInTrack drawing for reference.
- rightRail used when the train detector is placed on the top of the right rail. See the posInTrack drawing for reference.
- rightRailInside used when the train detector is placed near the right rail inside the track. See the posInTrack drawing for reference.
- rightRailOutside used when the train detector is placed near the right rail outside of the track. See the posInTrack drawing for reference.
- outside used when the train detector is placed outside of the track. It can be used for the equipment installed on the board of the train.
- outsideLeft used when the train detector is placed outside of the left rail. See the posInTrack drawing for reference and note that the train detector should be placed quite outside of the track, let's say 3 meters away.
- outsideRight used when the train detector is placed outside of the right rail. See the posInTrack drawing for reference and note that the train detector should be placed quite outside of the track, let's say 3 meters away.
- directionDetection used when the train detector has two coils to detect the train movement direction.
- model model of the train detector according to the manufacturer.
- axleCounting used to indicate if the train detector is an axle counter.
- virtual: (introduced with version 2.5) use this attribute to model a local dispatcher doing a visual train detection
Syntactic Constraints / Syntaktische Beschränkungen
- id: xs:ID, required
a string, starting with a letter (a..zA..Z) or an underscore (_),
followed by a non-colonized and non-spaced string consisting of letters, digits, points (.), dashes (-) or underscores (_) - code: xs:string, optional
- name: xs:string, optional
- description: xs:string, optional
- xml:lang: xs:language, language identification, optional
- pos: tLengthM (xs:decimal, 6 fraction digits, length value measured in meter); required; must be greater than or equal to zero, less than or equal to the track's length
- absPos: tLengthM (xs:decimal, 6 fraction digits, length value measured in meter); optional
- absPosOffset: xs:decimal, 6 fraction digits, length value measured in meter; optional
- dir: xs:string, generic type for more constrained direction statements: enumeration up, down, unknown; derived from tLaxDirection; optional
- ocpStationRef xs:IDREF, optional
- controllerRef xs:IDREF, optional
- detectionObject optional
- medium: tDetectorMedium (union of (restriction of xs:string, tOtherEnumerationValue), where the latter is defined as:an arbitrary string starting with 'other:' followed by at minimum two characters, white space not allowed for extending railML® enumeration lists; pattern: other:\w{2,}); optional
- posInTrack optional
- directionDetection xs:boolean, optional
- model xs:string, optional
- axleCounting xs:boolean, optional
- virtual: xs:boolean; optional
Best practice & Examples / Empfohlene Anwendung & Beispiele
Not yet described. / Noch nicht beschrieben.
Notes / Anmerkungen
General information on positioning
Positive pos values describe the distance from the track's begin. The track length is derived from the pos value in <trackEnd>.
The absolute mileage refered to by absPos is usually found on technical drawings of the track layout or on mileage posts next to the track.
Open issues / Offene Punkte/Pendenzen
Not yet described. / Noch nicht beschrieben.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Paul Darlington and David Fenner Train detection – the basics (external link)
- ↑ legal information institute (external link)
- ↑ Block signalling practice on a British railway (external link)
- ↑ Theeg, Gregor, and Sergej Vlasenko. "Railway signalling & interlocking." International Compendium. Hamburg, Eurail-press Publ 448 (2009) (external link)